Linear Search
Linear Search is the simplest way to search and check the elements in the list ![]() .
.
Flowchart:
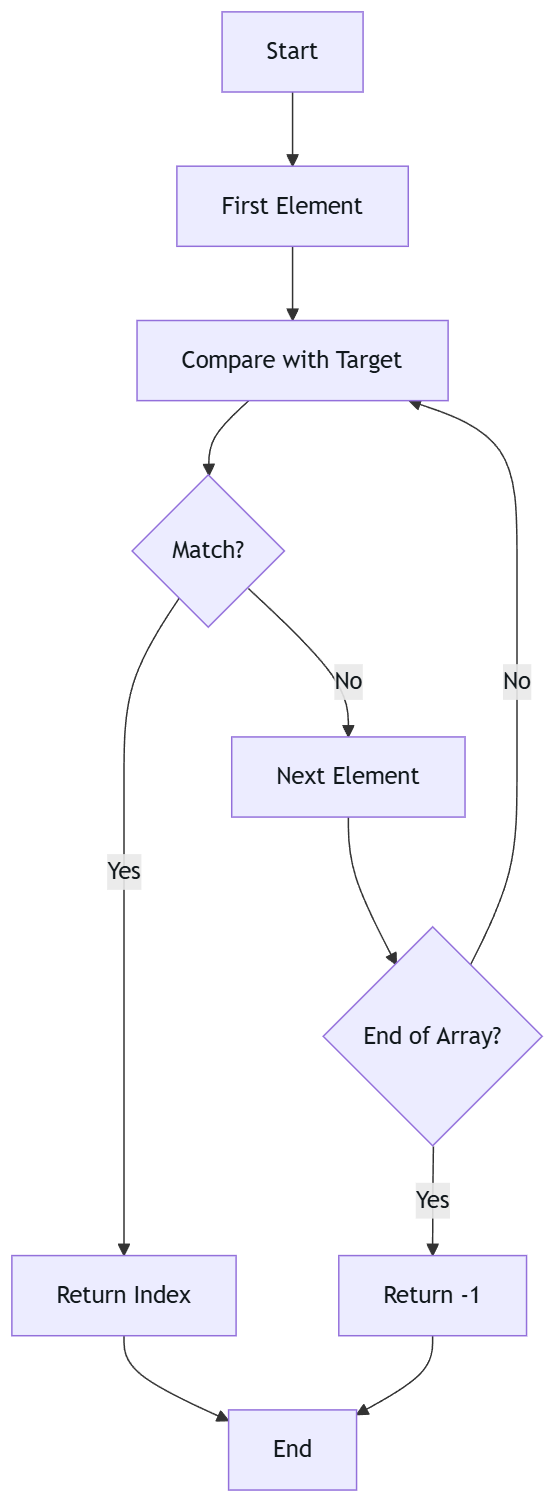
Let’s visualize the search process with an example array [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] and target 30:
| Step | Current Element | Compare with Target (30) | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 10 ≠ 30 | Move to next |
| 2 | 20 | 20 ≠ 30 | Move to next |
| 3 | 30 | 30 = 30 | Found! Return index 2 |
| 4 | 40 | Not reached | Search stops |
| 5 | 50 | Not reached | Search stops |
Implementation
Java Implementation
public class LinearSearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create test array
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int target = 30;
// Call linear search method
int result = linearSearch(arr, target);
// Print result
if (result == -1) {
System.out.println("Element not found");
} else {
System.out.println("Element found at index: " + result);
}
}
public static int linearSearch(int[] arr, int target) {
// Iterate through each element
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// If element found, return its index
if (arr[i] == target) {
return i;
}
}
// Element not found
return -1;
}
}
Python Implementation
def linear_search(arr, target):
for i in range(len(arr)):
if arr[i] == target:
return i
return -1
# Test the function
arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
target = 30
result = linear_search(arr, target)
if result == -1:
print("Element not found")
else:
print("Element found at index:", result)